Obesity has always been a risk factor for heart disease. Some of the most prominent epidemiologic studies in cardiovascular disease have conclusively demonstrated that being overweight increases the likelihood of having a stroke or heart attack. Even more concerning is that excess weight is associated with several other health problems, including high blood cholesterol and lipids, hypertension, and diabetes. These factors contribute to a person’s increased risk of acquiring heart disease, which is already high. As a result, an overweight patient with diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol is at a significantly increased risk of having a stroke or a heart attack. We know from the previous study that significant weight loss can reduce some of the hazards associated with diabetes.
The Relationship Between Obesity and Cardiovascular Health
Obesity and overweight are associated with several various types of cardiovascular illness, including high blood pressure, heart attack, atrial fibrillation, and stroke, among others. Extremely severe cardiac disease can result in heart failure. The heart cannot pump blood, depriving the body of enough oxygen-rich blood and oxygen-depleted blood.
Excess weight adds up more strain on the heart, which must work harder than usual to ensure that adequate blood is delivered throughout the body. As a result of the increased workload, the heart and accompanying structures, such as the arteries, veins, and ventricles, might suffer damage over time. The stress also harms the heart’s critical functioning.
What is the impact of bariatric surgery on the development of cardiac disease?
Previous research conducted over the last decade has demonstrated that bariatric surgery can reduce heart rate and blood pressure. Over ten years, we discovered that individuals who underwent bariatric surgery were nearly half as likely as those who did not have a stroke or heart attack as those who did not. The bottom line is that surgery reduces half the rate of major cardiovascular events.
Is surgery a risky procedure?
These treatments are performed through tiny incisions (laparoscopic or robotic), require an overnight stay, and result in a speedy return home. The likelihood of experiencing a severe problem is less than 1 percent. Compared to gallbladder removal, bariatric surgery looks to have a similar safety profile. Comparing the modest risk of complications with the considerable long-term improvement in heart disease shows that surgery provides a tremendous advantage. Recent research has revealed that individuals who undergo bariatric surgery live three to fifteen years longer than those who do not.
Risks and Prognosis for the Future
Dietary changes and weight-loss surgery can reduce the risk of heart disease and death while simultaneously improving the overall quality of life. Rapid weight loss can result in significant improvements; nevertheless, some cautions and hazards to consider.
For the remainder of their lives, patients who have had significant bypasses of the regular digestive process must adhere to to a healthy diet and exercise regimen for long term to maintain success of bariatric surgery. .
Because vitamins and minerals are not absorbed adequately after a gastric bypass procedure, there is a 30% chance of nutritional deficiencies occurring after the process. So you’ll have to supplement for the rest of your life to avoid malabsorption disorders like anemia and osteoporosis, which are both preventable.
Who is a candidate for surgery?
Although this is a poor method of determining weight and risk, most insurance firms classify weight based on a measurement known as body mass index. In Asian Patients with BMI greater than 35 with weight-related comorbidities or BMI of 40 without weight related comorbidities would be eligible for surgery under the policies of the majority of insurance companies. Several online calculators are used to determine one’s body mass index, and one should always check with the insurance provider to ensure that the policy will cover bariatric surgery. We are always glad to meet with patients and discuss their customized alternatives if they do not have Mediclaim, depending on their specific health history, requirements, and aspirations.
Adults who have the following conditions may benefit from bariatric surgery, according to guidelines released in 2013 by the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and the Obesity Society:
A body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher
OR
An obesity-related health concern such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, sleep apnea, and a BMI of 35 or higher is considered obese.
OR
A BMI of 30 or higher in conjunction with a significant health issue associated with obesity (only applies to gastric band surgery)
Long-term success after bariatric surgery is primarily dependent on adhering to the prescribed diet and exercise regimen. Some people find this problematic because it requires a lifelong commitment
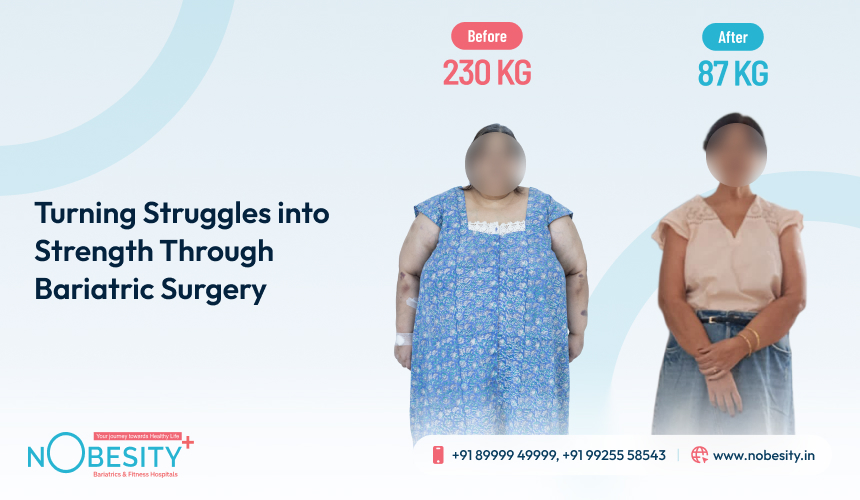
As a result of weight-reduction surgery, many patients experience rapid and significant weight loss. Depending on the procedure, it can occur one to two years after surgery.
Consult Dr. Manish Khaitan for any doubt or query related to weight loss surgery Call now: 8999949999