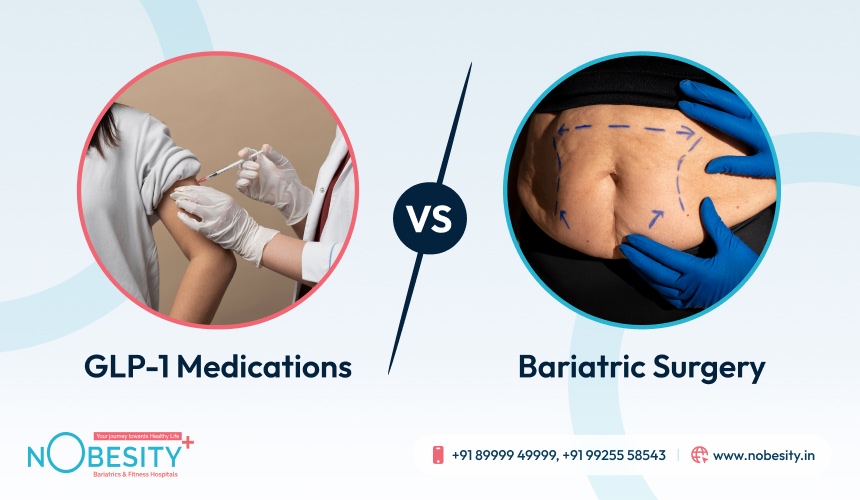
Bariatric Surgery vs GLP-1 Medications: Which Is the Right Choice for Long-Term Weight Loss?

From the moment many of us first heard about drugs like Semaglutide or Tirzepatide, it felt as though a lightbulb went off: a shot, an injection, and suddenly the weight started to drop. It sounded almost too good to be true—and in many ways, it was. These medications belong to a class known as GLP‑1 receptor agonists, originally developed to treat type 2 diabetes and regulate blood sugar dynamics. Their mechanism of action is fascinating: by mimicking a hormone released in the gut, they slow gastric emptying, suppress appetite, and improve insulin response—creating the impression of a “metabolic reset”. Suddenly, the reach of these drugs extended beyond diabetes clinics; they became the focal point of glossy weight-loss media stories in India, the U.S., Europe, and beyond.
But here’s where the reality diverges from the hype. A critical review indicates that while GLP-1 receptor agonists do promote weight loss, the numbers in real-world settings are modest compared to the transformation narrative so widely circulated. PMC+1 Further, their original authorisation and indication were for glucose-control—not for long-term, standalone obesity treatment. Many Indian patients who hoped for a one-and-done fix discover that support, follow-up, cost, and lifestyle changes still matter.
Even more, the regulatory story adds a cautionary note. In the U.S., the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently flagged concerns about unapproved products labeled as “for research use only” but sold directly to consumers, many claiming the same GLP-1-based magic. The message is clear: the promise is big, but the foundation requires scrutiny.
As we move into exploring “The Hidden Costs: Beyond the Needle and the Scale”, this narrative sets the scene for why a medication alone—despite its appeal—may not be the complete answer for sustained weight loss. The next chapter will step into what you may not have been told, helping you understand what this treatment offers—and where it stops.
The story of GLP-1 medications began not in weight-loss clinics but in diabetes research. Scientists found that a natural gut hormone, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), helps control blood sugar by stimulating insulin, slowing digestion, and signaling fullness to the brain. These modern medical treatments were developed to mimic this hormone and support better management of Type 2 diabetes.
Later, patients using these drugs reported unexpected weight loss due to reduced appetite, which shifted their use from diabetes treatment to mainstream weight-management therapy. However, these drugs were never originally designed for long-term obesity control. Their effect lasts only while the medication is taken, and stopping it often leads to weight regain. Research from the U.S. FDA and the National Library of Medicine highlights the same concerns: dependency, high cost, and side effects such as nausea or digestive discomfort.
Understanding these facts is key before choosing medication-based weight loss. It helps separate temporary appetite control from sustainable metabolic change — a distinction that becomes clearer as we explore the real costs behind the needle.
GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic a hormone naturally produced in the gut that signals fullness to the brain and slows digestion. This mechanism reduces appetite and helps control calorie intake effectively without drastic dieting. Their role as weight loss aids is supported by extensive research documenting their physiological effects across multiple populations.
Originally designed for blood sugar control in type 2 diabetes, GLP-1 drugs have evolved into important therapies for obesity treatment globally. Their approval for weight management spans markets in Europe, Asia-Pacific, and India, where increasing obesity rates have driven demand. Insights from Roots Analysis highlight this shift and its impact on global healthcare.
Despite benefits, GLP-1 medications present challenges such as dependency, rebound weight gain upon stopping treatments, high costs especially in emerging markets, and side effects like nausea or digestive discomfort. Regional reviews like those from MarketsandMarkets underline these critical issues impacting accessibility and adherence.
GLP-1 therapies are rapidly expanding in Europe, the Asia-Pacific region, including India and China, driven by rising obesity and supportive healthcare initiatives. Market dynamics differ markedly outside the US, with initiatives in India increasing awareness and availability. Detailed analysis from Grandview Research provides comprehensive data on these international trends.
When modern medical weight-management treatments began making headlines for rapid and sustainable weight loss, they were hailed as breakthroughs for individuals who had tried every diet and fitness routine with little success.. Marketing and social media promised a quick, effortless transformation through a weekly injection. But the real-world data tells a different story — smaller weight loss, higher costs, and uncertain long-term outcomes. Understanding this gap between promise and performance helps separate medical facts from marketing fiction.
Recognising these realities is essential before committing to GLP-1-based treatment. The next step lies in understanding the hidden costs — physical, financial, and emotional — that accompany these medications over time.
The journey with GLP-1 medications often begins with optimism but soon reveals deeper challenges. While effective for short-term weight loss, many users experience nausea, bloating, fatigue, and other digestive issues in the early months of treatment. Prolonged use may also increase risks such as gallbladder inflammation or pancreatitis.
Over time, the body adapts to appetite suppression, making results harder to sustain. Beyond physical effects, the financial and emotional burden of continuous medication—anxiety about missed doses, frustration over plateauing results, and the high cost of ongoing treatment—can take a toll. These realities show that while GLP-1s help reduce weight, they rarely address the underlying metabolic factors that drive long-term weight gain.
So much for the “easy fix” — here’s what often comes with it:
Real progress means moving beyond short-term control toward long-term change. When the focus shifts from temporary loss to genuine health transformation—restoring hormonal balance, improving nutrient absorption, and rebuilding metabolic strength—the body doesn’t just lose weight; it learns how to maintain it.
Lasting weight control is a question of physiology, not just willpower. The strongest evidence compares how far medications can take you versus how much the body can be reset through metabolic surgery. The picture that emerges is consistent across large trials and long follow-ups.
Clinical studies reveal that bariatric and metabolic surgeries achieve more substantial and lasting results than GLP-1 therapies. According to the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, surgical patients lose up to five times more weight at two years compared to those using semaglutide or tirzepatide, with sustained benefits for a decade or more, whereas most medication users regain weight once treatment stops.
Unlike GLP-1 drugs that temporarily suppress hunger, bariatric surgery triggers hormonal recalibration. Post-surgery, appetite-regulating hormones such as GLP-1 and PYY naturally increase, while ghrelin—the hunger hormone—decreases. This physiological reset enhances satiety, improves insulin sensitivity, and supports long-term metabolic stability.
The benefits of surgery extend far beyond visible weight change. Research shows higher rates of diabetes remission, better cardiovascular health, and improved quality of life in surgical patients compared to those relying solely on medication. Studies published in JAMA Network confirm that bariatric surgery significantly reduces the risk of heart failure, stroke, and hypertension in obese individuals with Type 2 diabetes.
Modern clinical consensus recognizes metabolic surgery and pharmacotherapy as complementary, not opposing, approaches. For many, GLP-1 therapy serves as an entry point to weight management or a preparatory phase before surgery. This integrated model aligns with the evolving understanding of obesity as a chronic metabolic condition, not a matter of willpower or appearance.
Science makes the distinction clear—while GLP-1 therapies can help begin the journey, surgery often provides the enduring reset the body needs for long-term metabolic health and stability.
Both GLP-1 therapies and bariatric surgery contribute to weight reduction, but they operate through very different mechanisms and produce distinctly different long-term outcomes. Understanding these contrasts helps patients and clinicians decide which approach delivers true, lasting change rather than short-lived control.
|
Factor |
GLP-1 Medications |
Bariatric /Metabolic Surgery |
| Results Over Time | Produces steady weight loss while in use, but progress often plateaus or reverses after discontinuation. | Delivers deeper, longer-lasting weight maintenance by changing how the body processes food and regulates energy. |
| Mechanism | Mimics a hormone to curb appetite and slow digestion—helpful, but temporary. | Alters gut-hormone signaling, resetting hunger cues and metabolism for sustained physiological change. |
| Risk and Reversibility | Non-invasive and reversible, yet side effects like nausea, fatigue, and digestive discomfort are frequent, along with dependency concerns. | Involves surgery, but outcomes are stable after recovery; procedures today are minimally invasive with structured follow-up care. |
| Impact on Overall Well-being | Improves short-term control and confidence, but results depend on strict adherence and affordability. | Enhances long-term health markers—blood sugar, heart health, and energy—while improving daily quality of life. |
Choosing the right path to lasting weight control depends on more than numbers on a scale—it depends on overall health, metabolism, and how the body adapts over time. While GLP-1 medications may offer short-term weight reduction or help manage pre-surgical preparation, bariatric surgery continues to be the most proven and enduring approach for long-term results.
Modern bariatric procedures are minimally invasive and performed with advanced laparoscopic techniques at NObesity, ensuring safety, precision, and faster recovery. These surgeries not only limit food intake but also reset hormonal signals, improve insulin sensitivity, and restore natural metabolic balance—delivering benefits that medications alone cannot achieve. For individuals struggling with obesity-related conditions such as Type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea, bariatric surgery has shown remarkable improvements in both physical health and emotional well-being.
Why bariatric surgery remains a trusted, long-term solution:
At its core, bariatric surgery is not a shortcut—it’s a science-backed intervention that addresses obesity from within. With skilled laparoscopic care at NObesity, patients don’t just lose weight; they regain control of their health, confidence, and quality of life for the long run.
Fear is often the last barrier between understanding and action. While evidence clearly supports bariatric surgery as a safe and effective treatment for obesity, emotional hesitation often overshadows medical facts. Recognizing the source of that hesitation helps patients make informed, confident decisions about their health.
The appeal of GLP-1 injections lies in their simplicity—no hospital stay, no incision, and no immediate risk. Yet, this perceived safety often ignores medical reality. Long-term studies show that continuous drug dependence, gastrointestinal side effects, and rebound weight gain are common once treatment stops.
By contrast, laparoscopic bariatric surgery is minimally invasive and performed under controlled medical environments, offering measurable metabolic improvement. It doesn’t suppress appetite artificially; it restores the body’s natural hunger regulation, improving insulin response and long-term weight stability.
Modern bariatric procedures are among the safest elective surgeries in medicine, with risk rates comparable to gallbladder or knee surgery. Recovery times are short, often requiring only a few days of hospitalization and a few weeks for full activity.
The hesitation usually stems not from medical facts but from misconceptions and social stigma—fears of complications or external judgment. At NObesity, patients receive detailed preoperative counseling, personalized nutritional guidance, and psychological support to ease the transition from anxiety to assurance.
What reassures patients most:
Patients who undergo bariatric surgery often experience transformations that go far beyond weight loss. Clinical evidence shows significant improvements in Type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and heart health, along with renewed energy, mobility, and emotional balance—proving that surgery changes how the body functions, not just how it looks.
At NObesity, patients often share how surgery helped them walk pain-free, reduce lifelong medications, and rediscover confidence in everyday life. Their journeys reflect how medical expertise, consistency, and self-belief together create lasting results.
You can explore these real transformations in our patient success stories, where each narrative demonstrates that with the right guidance and commitment, bariatric surgery restores health, confidence, and control that truly last.
Real transformation isn’t found in trends—it’s built through science, consistency, and care. Sustainable weight loss begins when treatment moves beyond appetite control to address the body’s underlying metabolic balance. True progress comes from medically guided decisions made with expertise and empathy, not commercial promises or overnight fixes.
With a trusted medical framework like that followed at NObesity, patients experience a structured approach—comprehensive evaluation, multidisciplinary supervision, and long-term follow-up that prioritizes health over haste. It’s this alignment of science and support that turns temporary success into lasting wellness.
Because the right choice doesn’t just reduce weight—it restores life.